KAIST researchers use an array of microLEDs to create a wearable skin care patch
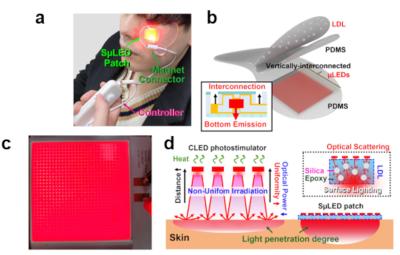
Researchers from Korea-based KAIST institute developed a microLED-powered wearable patch that acts as an UV-induced inhibitor for melanogenesis, the creation of brown or dark pigments that can lead to skin diseases.
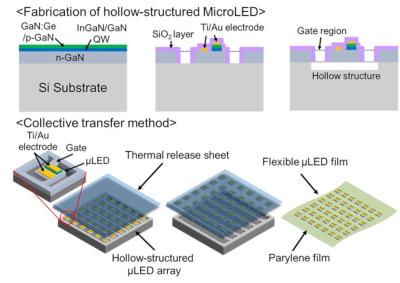
LEDs have been used to photo-stimulate in skin care, but normal devices cannot conform to the skin shape, they operate from a distance which is problematic. If the patch is connected to the skin, it achieves much more effective photo-treatment. In this research, the team fabricated a 4x4 cm2 wearable device made from an array of 100-micron sized microLED chips, vertically interconnected for high flexibility.